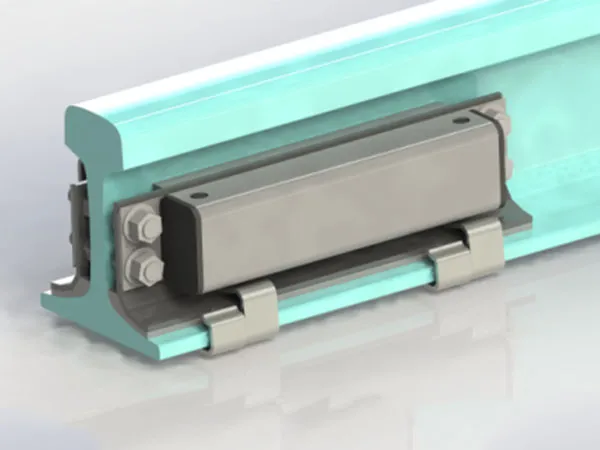
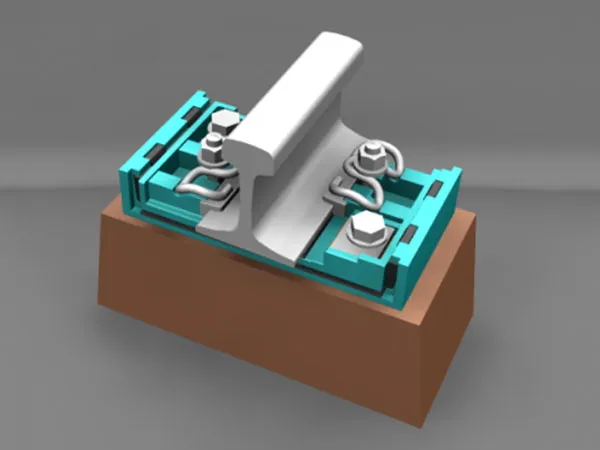
Overview of Tie Plates
A tie plate is a metal component installed between railway sleepers (or rail sleepers) and the rail base. Its main functions are:
To distribute the pressure of the rail on the sleepers, preventing excessive stress and damage.
To maintain track gauge stability, preventing lateral or longitudinal rail movement.
To increase the contact area between the rail and the sleeper, reducing localized stress concentration.
Used in conjunction with the fastening system, it achieves rail fixation and vibration damping.
In short, the tie plate is an indispensable pressure-bearing and fixing element in the track system.
Main Functions of Tie Plates
Pressure Distribution: When the rail is subjected to train loads, the pressure at the bottom is transmitted to the sleepers. The tie plate, with its large contact area, distributes the pressure, reducing localized stress on the sleepers and extending their lifespan.
Preventing Rail Displacement: Tie plates are usually used with bolts or fasteners to fix the rails, helping to maintain track gauge, preventing lateral or longitudinal rail slippage, and improving traffic safety.
Vibration Damping: Modern tie plates are often used in conjunction with elastic gaskets (such as rubber or polyurethane gaskets) to reduce vibration transmission between the rail and sleepers, thus reducing noise and structural fatigue.
Sleeper Protection: For wooden or concrete sleepers, tie plates prevent the rail from cutting into the sleeper, avoiding wear and breakage.
Classification of Tie Plates
Railway tie plates can be classified into several categories according to material, shape, and function:
1) By Material
Steel Tie Plates: Most commonly used, high strength, suitable for heavy-haul railways.
Cast Iron Tie Plates: High hardness, good wear resistance, but lower toughness, suitable for low-speed lines or light-load tracks.
Composite Tie Plates: Combine metal and elastic materials such as rubber and polyurethane, balancing load-bearing and vibration damping.
2) By Shape
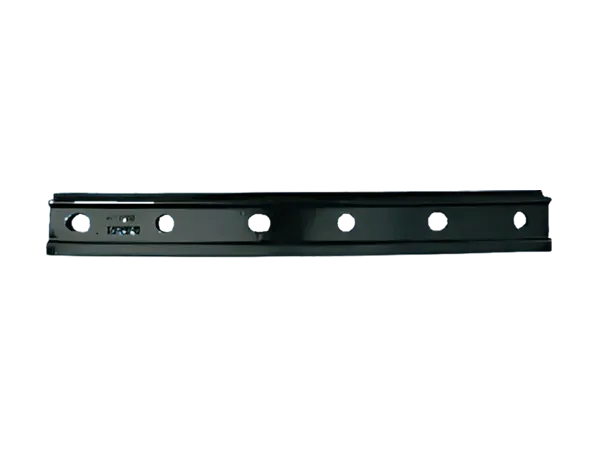
Flat Plate: Simple structure, directly bearing pressure, mainly used in low-speed railways.
Sloped/Corrugated Plates: Increase friction to prevent lateral movement of the rail.
Plates with Holes: Facilitate bolting of rails and can be used in conjunction with elastic washers.
3) By Function
Standard Pressure Plates: Primarily distribute pressure and do not provide special vibration damping.
Elastic Vibration Damping Plates: Typically include rubber or polyurethane pads and are used in high-speed railways or noise-sensitive areas.
Gap Fixing Plates: Specifically designed to ensure track gauge accuracy and often integrated with the fastening system.
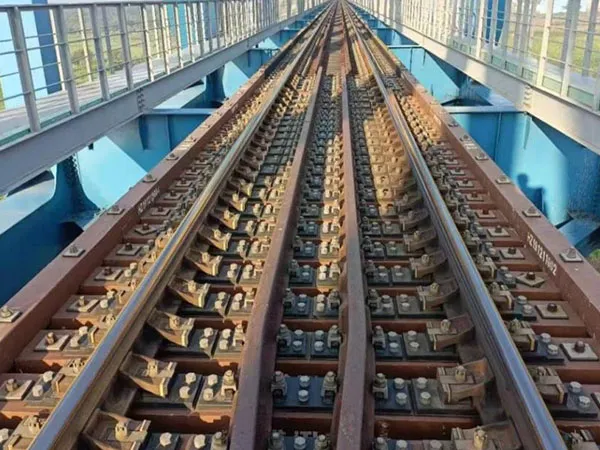
Installation Position of Tie Plates in the Track Structure
Sleeper Types
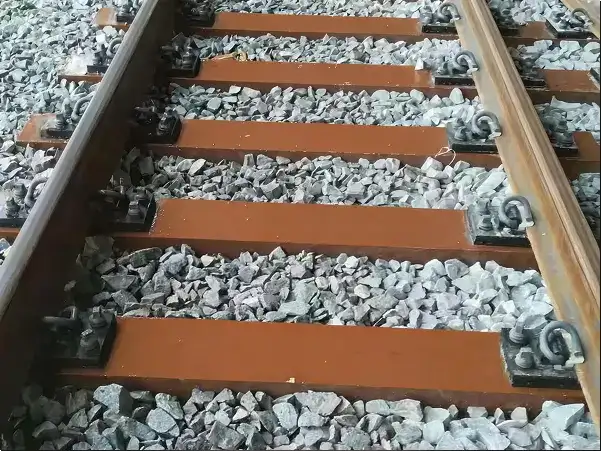
Wooden Sleepers: The tie plate is placed directly on the wooden sleeper, and the rail is fixed to the plate with bolts or fasteners.
Concrete/Composite Sleepers: Holes are usually pre-embedded in the sleeper, and the tie plate is fixed to the sleeper with bolts. Elastic washers can also be used.
Rail Types
Tie plates are typically adapted to different rail widths (e.g., UIC 54, UIC 60, etc.) to ensure stable rail stress.
Tie plates are often used in conjunction with bolts, spring clips, or vibration-damping fasteners to achieve fixation, anti-slip properties, and vibration reduction.
Key Design Considerations for Tie Plates
Load Capacity: The thickness and material of the tie plate must meet the train load requirements.
Corrosion Resistance: Hot-dip galvanizing or spray coating is typically used for corrosion protection to adapt to outdoor environments.
Abrasion Resistance and Toughness: Ensure long-term use without deformation or breakage.
Elastic Fit: In modern track systems, the combination of tie plates and elastic pads improves comfort and stability.
Application Trends of Tie Plates in Modern Railways
High-Speed Rail Lines: Steel-rubber composite tie plates are used to achieve high load and high vibration reduction requirements.
Urban Rail Transit: Emphasis is placed on low noise and low vibration; the tie plate and elastic fastener system are optimized as a whole.
Heavy-Haul Freight Railways: Thick steel plate tie plates are preferred to improve abrasion resistance and stability.