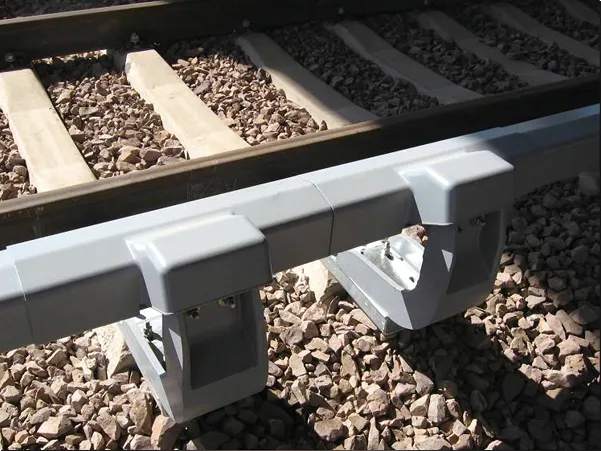
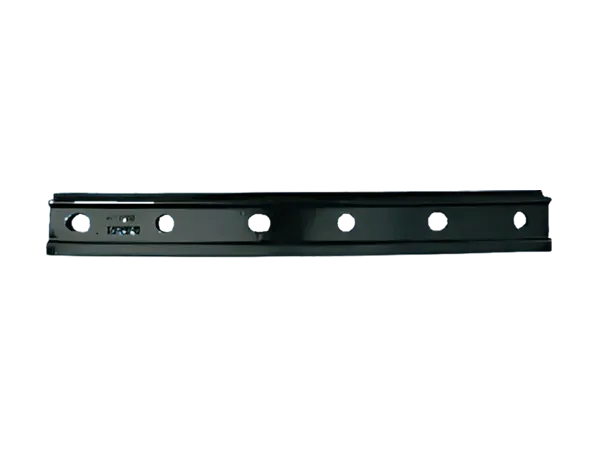
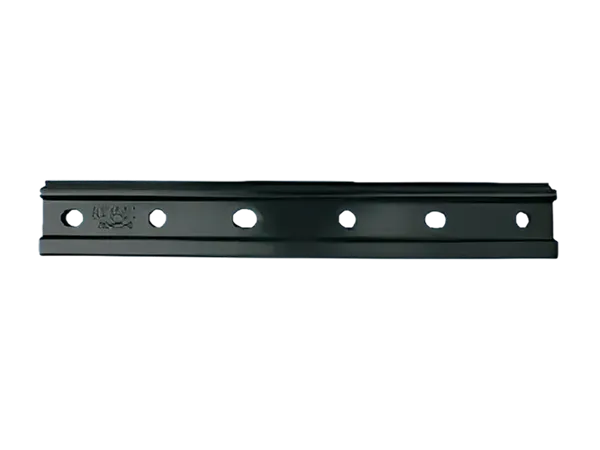
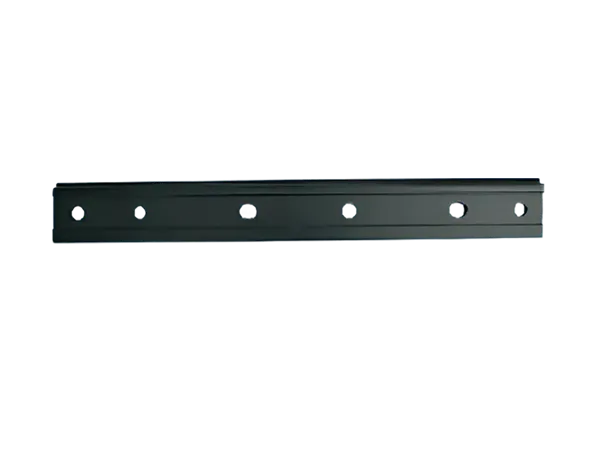
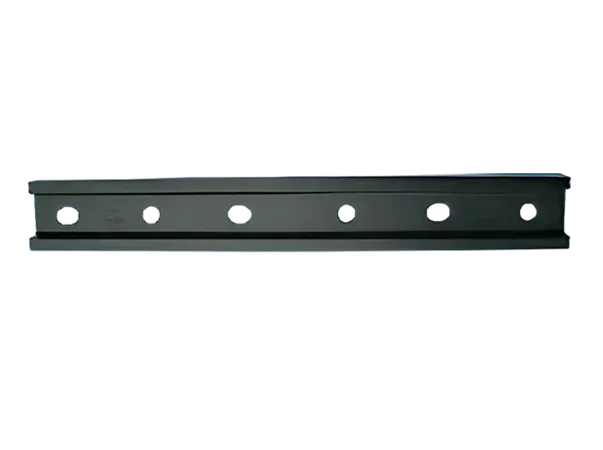
Introduction to Fishplates (Rail Connectors)
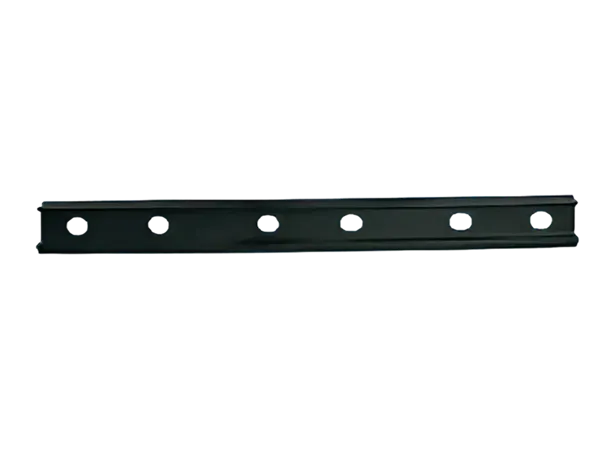
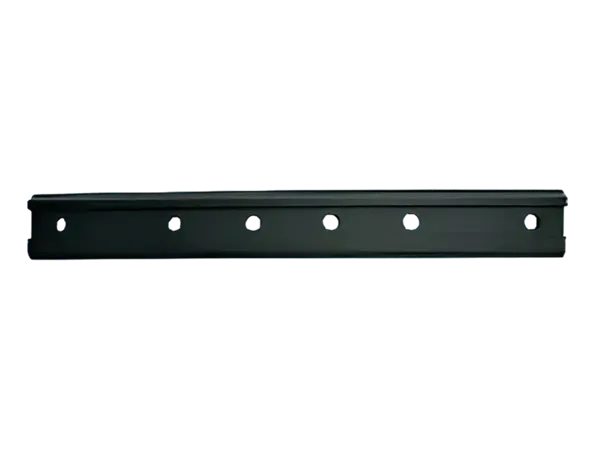
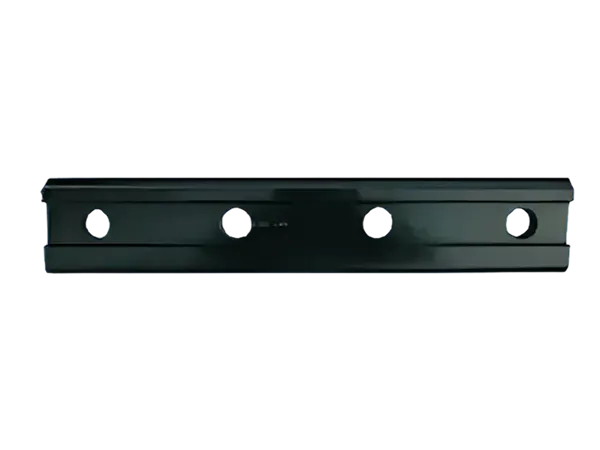
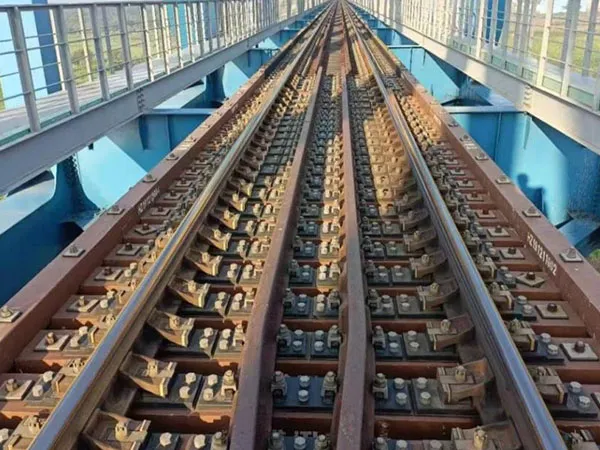
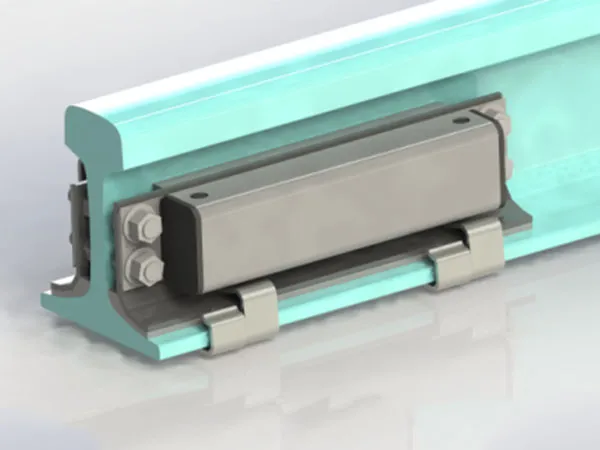
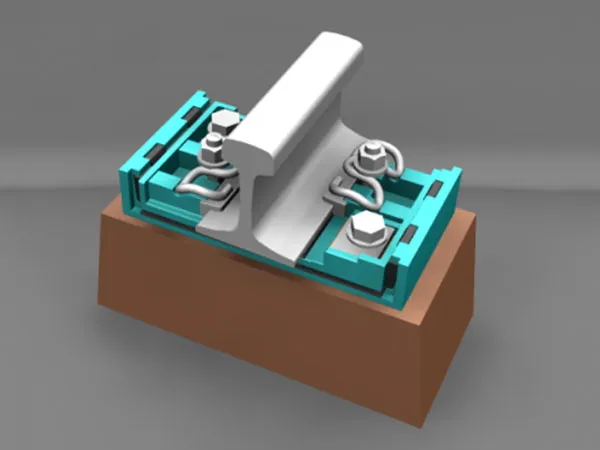
Definition: A fishplate, also known as a rail connector, is a metal plate used in railway track systems to connect two adjacent rail sections. It is typically fixed to the fishtail (end) of the rail, and the rails are tightly connected by bolts to form a continuous railway line.
Basic Characteristics:
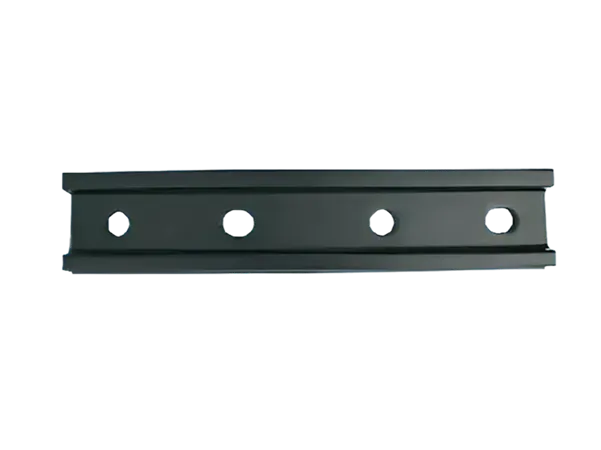
Its shape is usually long and narrow, with a width similar to the width of the rail base plate, moderate thickness, and rectangular or slightly curved ends.
Bolt holes are drilled at both ends for fixing the rails.
The material is generally high-strength carbon steel or alloy steel to ensure load-bearing capacity and wear resistance.
Main Functions of Fishplates
Connecting Rails
It securely connects the ends of adjacent rails, forming a continuous track and ensuring smooth train operation.
Transferring Loads
Train loads are transferred to the ballast bed through the rails. The fishplate ensures even force distribution between the rails, reduces stress concentration at the ends, and prevents rail end misalignment.
Maintaining Track Geometry
Maintaining consistent track gauge, preventing excessive track clearance or misalignment, and ensuring smooth and safe train operation.
Easy Installation and Maintenance
Fishplates allow for quick assembly and disassembly during rail replacement, maintenance, or track extension, simplifying the construction process.
Material and Performance Requirements for Fishplates
Common Materials:
Carbon structural steel (e.g., Q235, Q345
Alloy steel (for high-strength or heavy-load rails)
Performance requirements:
High strength, fatigue resistance: able to withstand repeated train loads
Corrosion resistance: oxidation resistant, rust prevention
Wear resistance: reduces wear on bolt holes and ends
High precision: ensures smooth rail joints
Structural Types of Fishplates
Depending on their application and design, fishplates can be classified into the following types:
Ordinary Fishplate
Used for general railway lines
Both ends are fixed to rails, with bolt holes arranged symmetrically.
Heavy-duty Fishplate
Used for heavy-load rails or high-speed railways
Increased plate thickness, more bolt holes, stronger load-bearing capacity
Insulated Fishplate
Used for electrified railways and track circuits
The plate has an insulating layer in the middle to prevent short circuits of track current.
Adjustable Fishplate
Used for track adjustment or temperature stress compensation
Can finely adjust rail gaps or height.
Installation Method of Fishplates
Align the rail ends
Ensure the rail ends are straight, clean, and without obvious gaps.
Place the Fishplate
Snap the fishplate into both ends of the rail, ensuring the holes are aligned.
Secure the Bolts
Use high-strength bolts and tighten them, typically using a cross-tightening method to ensure even stress distribution.
Check Track Flatness
Confirm that the rail ends are aligned and the gauge is consistent; make minor adjustments if necessary.
Precautions for Use
Regularly check for loose bolts: Loose bolts may cause the rail gap to widen, affecting train stability.
Corrosion Protection: Especially in humid or coastal areas, the fishplate should be oiled or galvanized.
Avoid Fatigue Damage: Prolonged heavy-load operation may cause the fishplate to crack; it should be replaced promptly.
Temperature Stress Considerations: In high-temperature or extremely cold environments, the thermal expansion and contraction of the rail may require the use of expansion joints or adjustable fishplates.
Summary
Although a small component in the railway track system, the fishplate plays a crucial role in rail connection, load transfer, and track stability. Proper material selection, correct installation, and regular maintenance are key to ensuring safe railway operation and extending track life.