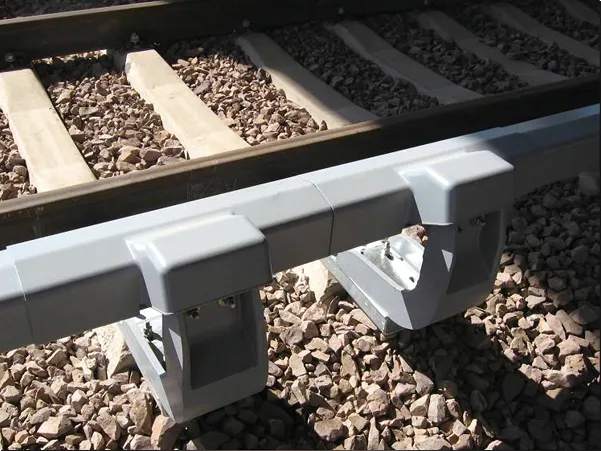
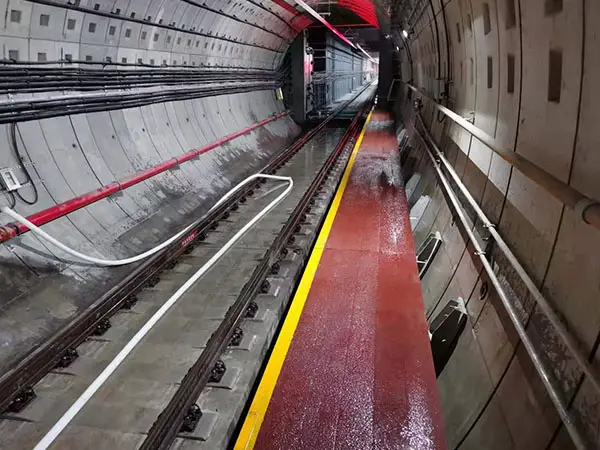
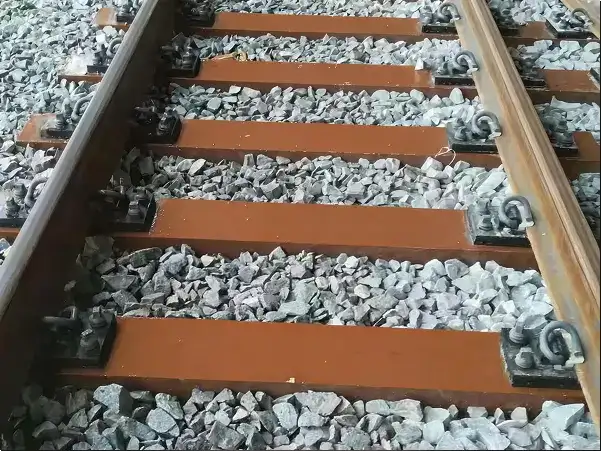
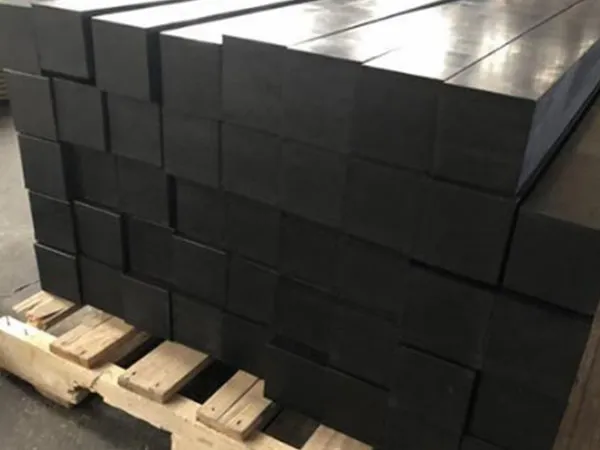
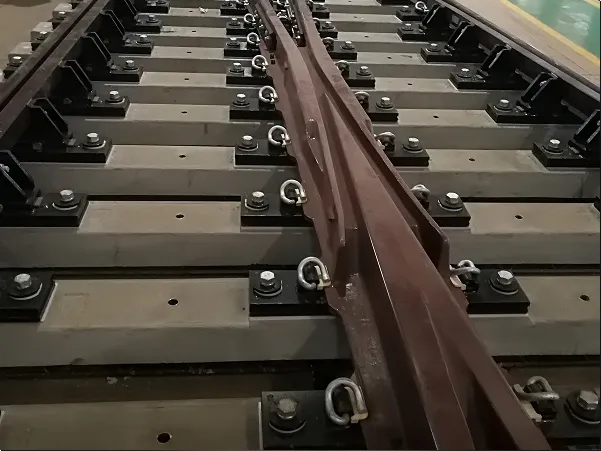
As global rail infrastructure continues to modernize, traditional timber and concrete sleepers are increasingly challenged by durability, sustainability, and lifecycle cost issues. Synthetic railway sleepers, also known as plastic or composite railway sleepers, have emerged as a reliable and future-ready alternative.
Synthetic railway sleepers (also known as composite sleepers or composite railroad ties) are modern alternatives to traditional wood, concrete, or steel sleepers. They are engineered from advanced composite materials to offer enhanced durability and performance.
In this article, we explain what synthetic railway sleepers are, explore their key benefits, examine the materials used, and highlight their main applications across modern railway systems.
What Are Synthetic Railway Sleepers?
Synthetic railway sleepers are engineered track support components manufactured from recycled plastics, polymer composites, or fiber-reinforced materials. They are designed to replace conventional wooden, concrete, or steel sleepers while maintaining compatibility with existing rail infrastructure.
Unlike traditional timber sleepers, synthetic sleepers are:
Resistant to moisture, rot, insects, and chemicals
Dimensionally stable in varying climates
Designed for long-term performance with minimal maintenance
Because of these advantages, synthetic sleepers are increasingly used in mainline railways, bridges, turnouts, tunnels, and urban transit systems.
Key Benefits of Synthetic Railway Sleepers
1. Long Service Life and Durability
Synthetic railway sleepers typically offer a service life of 40–60 years, significantly outperforming timber sleepers. They do not crack like concrete or corrode like steel, making them ideal for harsh operating environments.
Key durability advantages include:
No rot or decay
High resistance to UV radiation and moisture
Excellent fatigue and impact resistance
2. Low Maintenance and Lifecycle Cost
While the initial cost of synthetic sleepers may be higher than timber, their total lifecycle cost is substantially lower. Reduced replacement frequency and minimal maintenance requirements lead to long-term savings for rail operators.
This makes synthetic sleepers especially attractive for:
Remote rail lines
High-traffic corridors
Locations with limited maintenance access
3. Environmental Sustainability
Sustainability is a major driver behind the adoption of synthetic railway sleepers. Most products are manufactured using recycled plastics, helping reduce landfill waste and deforestation.
Environmental benefits include:
Reduced demand for hardwood timber
Recyclable at end of life
Lower carbon footprint over the full lifecycle
4. Excellent Track Performance
Synthetic sleepers provide consistent load distribution and vibration damping, improving overall track stability. Their elastic properties help reduce noise and vibration, which is especially important in urban rail and metro systems.
They also offer:
Strong rail fastener retention
High dimensional accuracy
Stable gauge control
5. Easy Installation and Compatibility
Synthetic railway sleepers are designed to be fully compatible with standard rail fasteners, ballast profiles, and installation equipment. This allows seamless replacement of timber sleepers without major infrastructure changes.
In many cases, they are lighter than concrete sleepers, improving:
Handling efficiency
Installation speed
Worker safety
Common Materials Used in Synthetic Railway Sleepers
Recycled Plastic (HDPE, LDPE)
High-density and low-density polyethylene are widely used due to their:
Moisture resistance
Chemical stability
Cost-effectiveness
These materials are ideal for general track sections and light-to-medium load applications.
Polymer Composite Materials
Composite sleepers combine plastics with glass fiber, mineral fillers, or rubber additives to enhance mechanical strength and stiffness. They are suitable for heavier axle loads and demanding rail conditions.
Fiber-Reinforced Plastics (FRP)
FRP sleepers deliver high structural performance and are often used in:
Railway bridges
Turnouts and switches
High-stress track sections
They offer excellent load-bearing capacity while maintaining corrosion resistance.
Applications of Synthetic Railway Sleepers
Mainline and Heavy Haul Railways
Synthetic sleepers are increasingly used on mainline tracks where long-term durability and reduced maintenance are critical.
Railway Bridges and Tunnels
In environments exposed to moisture, chemicals, or limited ventilation, synthetic sleepers outperform timber and steel alternatives.
Switches, Crossings, and Turnouts
Their high dimensional stability and fastener-holding strength make synthetic sleepers ideal for complex track geometries.
Urban Transit and Metro Systems
Low noise, vibration reduction, and environmental benefits make synthetic sleepers a preferred solution for:
Subways
Light rail
Tram systems
Industrial and Mining Railways
In harsh industrial environments, synthetic sleepers resist oil, chemicals, and extreme weather better than traditional materials.
Synthetic vs Traditional Railway Sleepers: A Quick Comparison
Feature
|
Synthetic Sleepers
|
Timber Sleepers
|
Concrete Sleepers
|
Service Life
|
40–60 years
|
15–25 years
|
30–40 years
|
Moisture Resistance
|
Excellent
|
Poor
|
Good
|
Maintenance
|
Very low
|
High
|
Medium
|
Sustainability
|
High
|
Low
|
Medium
|
Weight
|
Medium
|
Light
|
Heavy
|
Why Synthetic Railway Sleepers Are the Future of Rail Infrastructure
With growing pressure on rail operators to improve safety, sustainability, and cost efficiency, synthetic railway sleepers offer a proven and scalable solution. Their long lifespan, environmental benefits, and excellent performance make them an ideal choice for both new rail projects and track renewal programs.
As railway networks continue to expand worldwide, synthetic railway sleepers are set to play a critical role in building resilient and future-proof rail infrastructure.