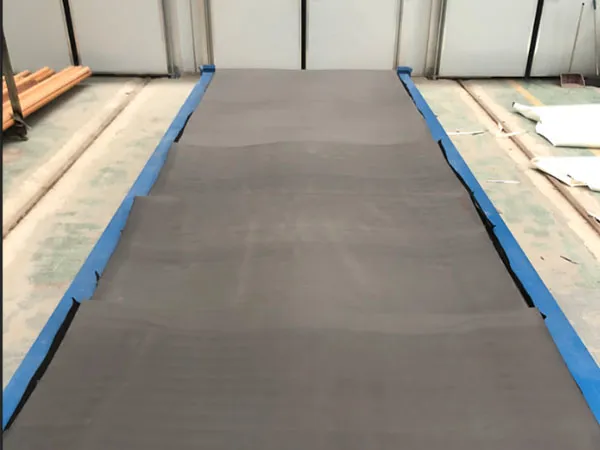
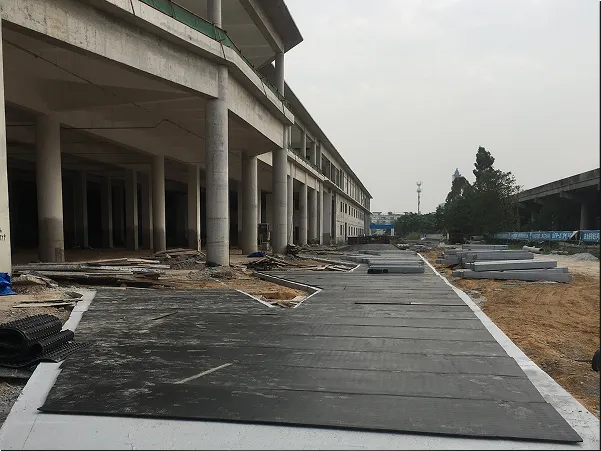
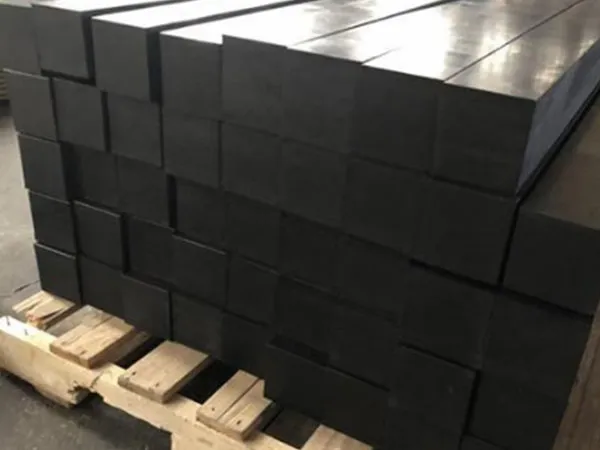
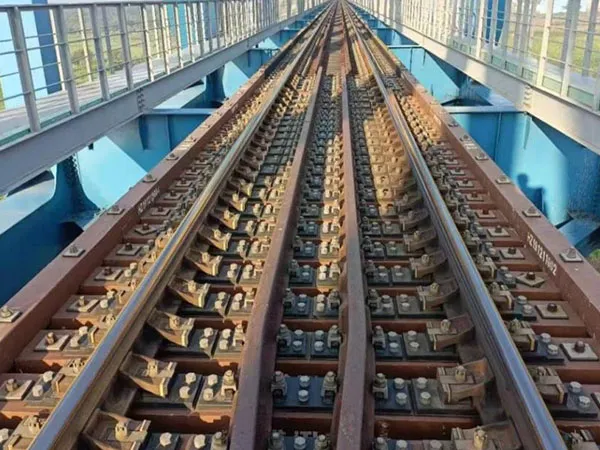
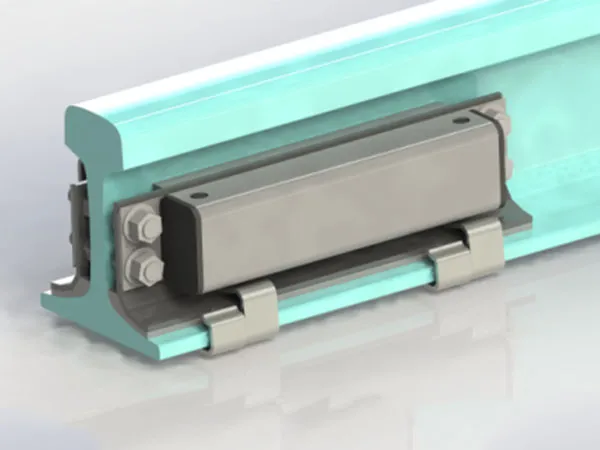
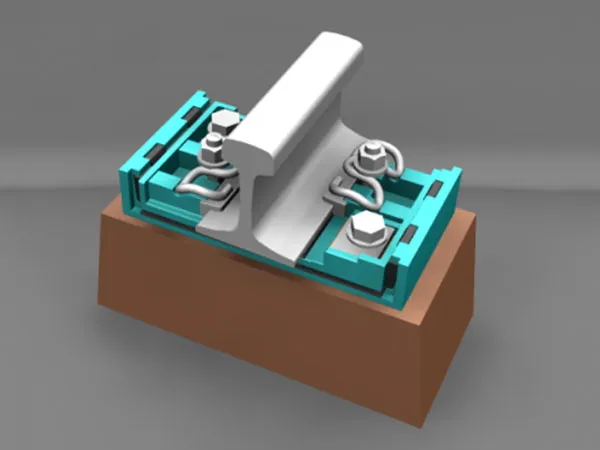
Rubber Pads Details
Rail rubber pads, also known as track pads, are indispensable elastic elements in railway fastening systems. They act like "shock absorbers" for the track, installed between the rails and sleepers (or steel pads).
Main Functions
Vibration Reduction and Noise Reduction
Rubber pads absorb the impact and vibration generated by train operation, reducing the vibration energy transmitted to sleepers and the roadbed, thereby reducing noise pollution.
This is particularly important for high-speed railways, subways, or urban light rail, as it improves passenger comfort.
Sleep Protection
Distributes rail pressure, reduces localized stress concentration on sleepers, and lowers the risk of sleeper cracking or breakage.
Especially suitable for wooden sleepers, concrete sleepers, or composite material sleepers.
Improved Track Stability
Prevents track slippage and longitudinal rail movement by increasing the coefficient of friction between the rail and sleepers.
Improves the elasticity and stability of the overall track structure.
Corrosion Resistance and Weather Resistance
Rubber materials have excellent waterproof and corrosion-resistant properties, extending the lifespan of track components.
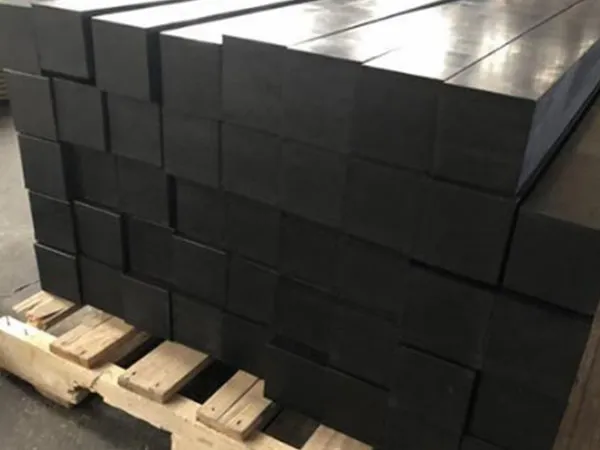
Materials and Types
Rubber pads are typically made of high-strength rubber (such as natural or synthetic rubber), and their hardness and thickness can be adjusted according to the operating environment. Common types include:
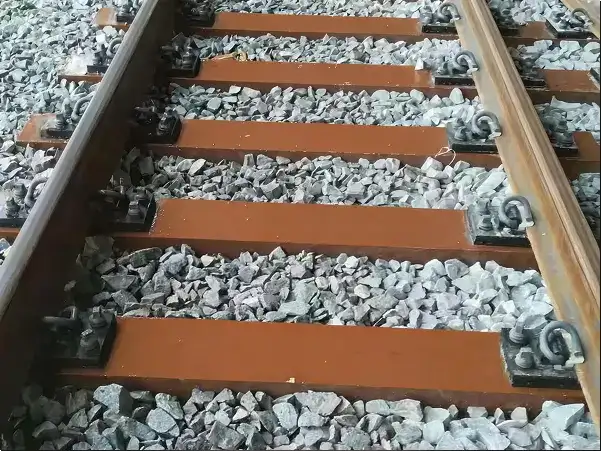
Standard Railway Rubber Pads
Used for standard tracks, typically 6–15 mm thick.
The main function is to cushion pressure and reduce vibration.
High-Speed Railway Special Pads
Material is specially formulated for high temperature and wear resistance.
Generally thinner, but with higher elasticity and durability to withstand high-frequency train loads.
Elastic Composite Pads
Made of rubber and composite materials such as polyurethane.
Provides stronger pressure resistance and elasticity, commonly used in bridges, turnouts, or special track structures.
Threaded or Grooved Pads
The surface is designed with threads or grooves to increase friction between the rail and the pad, further improving track stability.
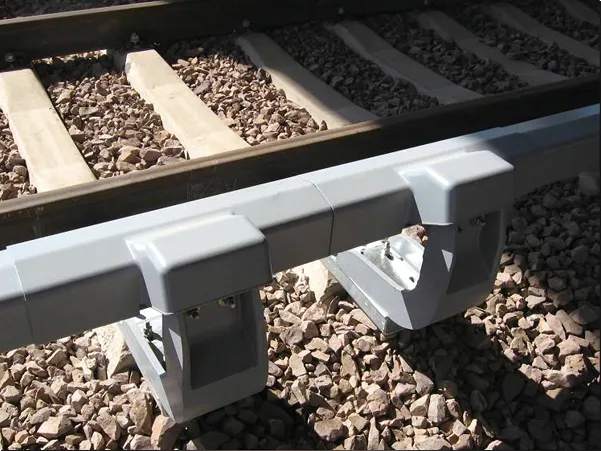
Installation Location and Method
Installation Location: Rubber pads are typically placed between the rail base and the sleepers.
Installation Method:
Place the pad flat on the sleepers.
Ensure the pad is in full contact with the rail base.
The rails are secured to the pads using a standard fastening system.
In turnout, bridge, or track repair, the installation of rubber pads requires attention to dimensional matching and load-bearing capacity.
Advantages
Extended Track Life
Reduces sleeper breakage and rail wear, increasing track lifespan.
Improved Running Comfort
Effectively reduces vibration and noise, improving the riding experience.
Compatible with Various Sleepers
Can be used with wooden sleepers, concrete sleepers, and composite sleepers.
Strong Environmental Adaptability
Corrosion-resistant, waterproof, and UV-resistant, adaptable to various climatic conditions.
Low Maintenance Costs
Easy installation, long service life, reducing track maintenance frequency.
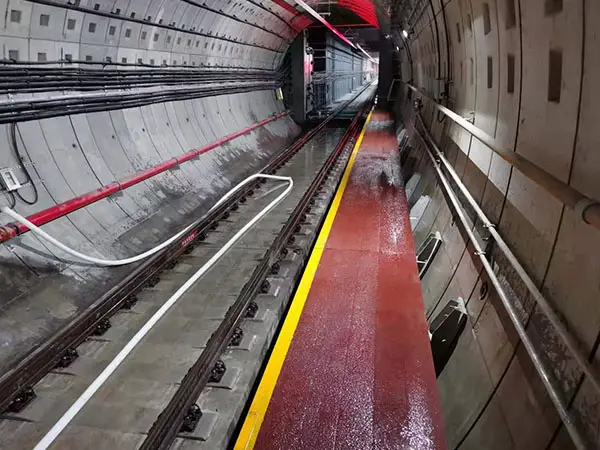
Typical Application Scenarios
High-speed railway main lines
Urban subways and light rails
Special track structures such as turnouts, bridges, and tunnels
Vibration-sensitive areas, such as tracks near residential areas and hospitals.