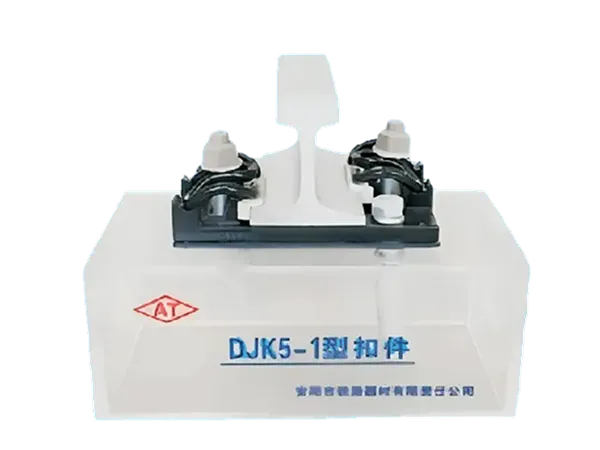
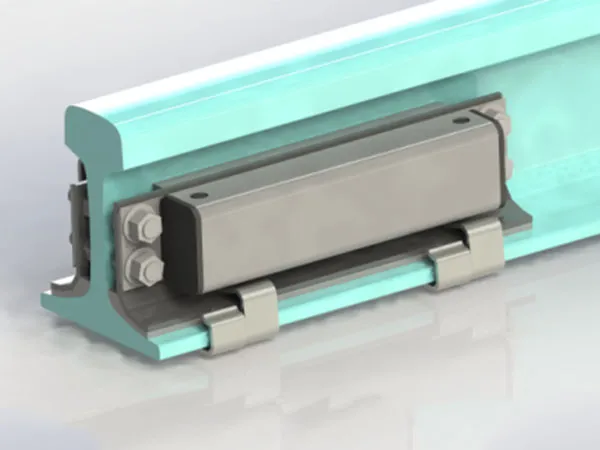
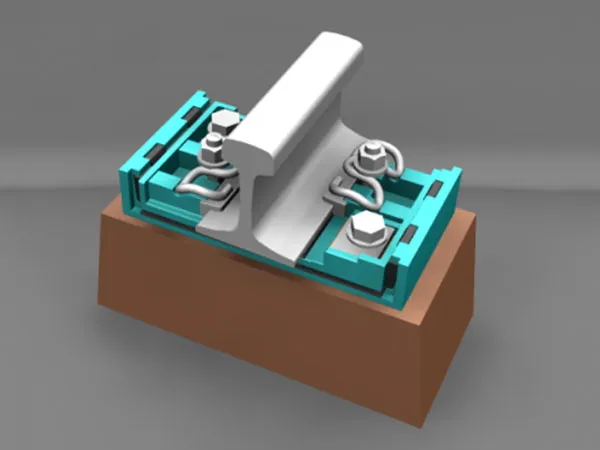
What are Rail Clamps?
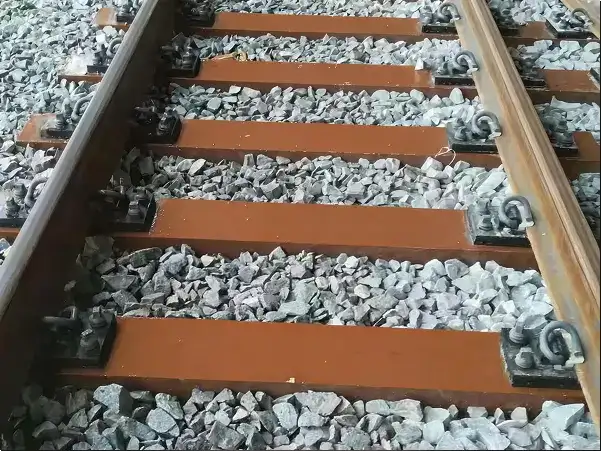
Rail clamps, also known as track fasteners or track fasteners, are an important component of railway track systems. They are used to fix the rails, maintain track gauge, reduce track movement, and work with sleepers and other fastening systems to ensure the safety and stability of train operation. They are typically installed on the bottom or side of the rails, clamping or securing the rails to the sleepers or track foundation.
Simply put, rail clamps are like "fastening bolts" for the rails, ensuring that the rails do not move laterally or longitudinally under train loads.
Main Types of Rail Clamps
Based on their design and purpose, rail clamps can be divided into several categories:
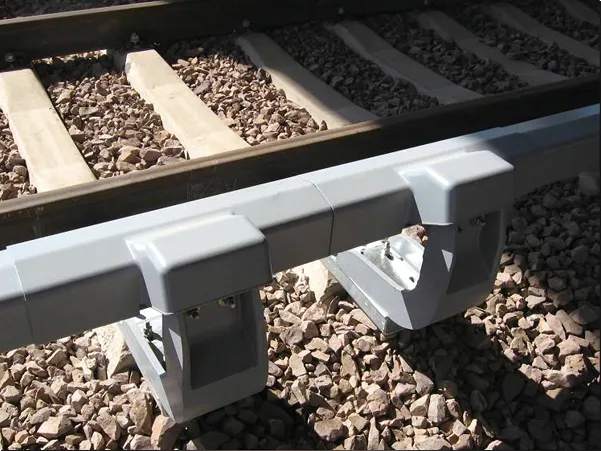
(1) Standard Rail Clamps
Used for ordinary railway lines.
The clamps are fixed to the sleepers with bolts, clamping the rail base plate.
Features: Simple structure, easy installation, and low cost.
(2) Elastic Rail Clamps/Spring Clips
Built in elastic material or spring elements, allowing slight movement of the rail under load.
Functions:
Absorbs vibration and shock
Reduces rail wear
Improves ride comfort
Commonly used in high-speed or heavy-haul railway lines.
(3) Heavy-duty/Special Rail Clamps
Specifically designed for heavy-haul freight lines, port tracks, or bridge tracks.
More robust construction, higher clamping force, and wear-resistant.
Some models can be used with vibration damping pads for vibration control.
(4) Adjustable Rail Clamps
Adjustable clamping force for easy rail maintenance or gauge adjustment.
Advantages: Greater flexibility in track maintenance and upgrades.
Functions and Roles of Rail Clamps
Rail clamps play several key roles in railway track systems:
Securing Rails
They ensure that the rails do not move longitudinally (in the direction of train movement) and laterally (in the direction of gauge), maintaining the track geometry.
Vibration and Noise Reduction
Used as elastic clamps or in conjunction with vibration damping pads, they absorb vibrations and noise generated by train operation.
Improving Train Safety
They prevent track displacement, gauge instability, or track loosening, reducing the risk of derailment.
Extending Track Lifespan
They distribute train loads, reducing direct impact between rails and sleepers, and improving the overall durability of the track structure.
Commonly Used Materials
Rail clamps are typically made of high-strength, wear-resistant materials to ensure clamping force and service life.
Material
|
Features
|
Carbon steel / Alloy steel
|
High strength, wear-resistant, and can be heat-treated to increase hardness.
|
Spring steel
|
It has good elasticity and is suitable for the design of elastic clamps.
|
Cast steel / Forged steel
|
High load-bearing capacity, suitable for heavy-load lines
|
Anti-corrosion coatings (such as galvanizing, powder coating)
|
Corrosion resistant, suitable for long-term outdoor use
|
Installation and Maintenance
Installation:
Place the rail clamps on the corresponding positions on the rail base plate or sleepers.
Adjust the clamping angle and pressure.
Secure with bolts or nuts.
Maintenance:
Regularly check the clamps for looseness, corrosion, or damage.
For elastic clamps, check for spring fatigue.
Replace damaged or aged clamps promptly to ensure track safety.
Application Scenarios of Rail Clamps in Track Systems
High-speed railways (requiring high stability and vibration reduction)
Heavy-haul freight lines (bearing high loads)
Port, mining, and industrial special tracks (high wear resistance and corrosion resistance requirements)
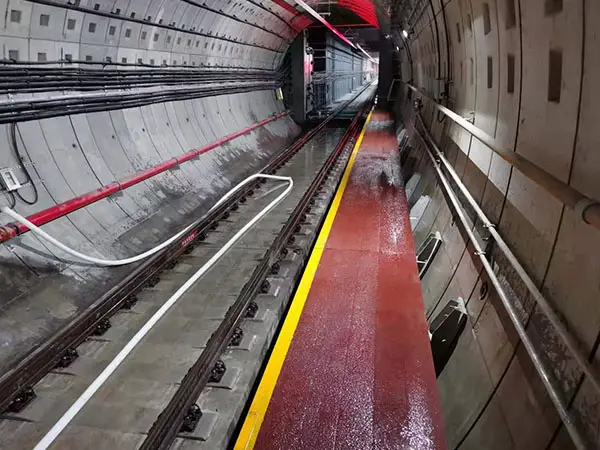
Bridge or tunnel tracks (special environments, corrosion resistance and vibration control)
Selection Considerations
When selecting rail clamps, consider the following factors:
Rail type: Different rail types have different base plate widths and thicknesses, requiring matching clamp sizes.
Load requirements: Heavy-haul lines require high-strength or elastic clamps.
Rail environment: Environments such as humid, coastal, or chemically corrosive environments require anti-corrosion materials or special coatings. Ease of maintenance: Adjustable or easily disassembled design facilitates routine maintenance.
Vibration control: Whether vibration damping pads or rubber pads are required.
In summary, rail clamps are indispensable fasteners in railway track systems, ensuring track geometry stability and directly impacting vibration control, noise reduction, and track lifespan. Different types and materials of rail clamps can be selected based on track type, load conditions, and environmental requirements to achieve optimal performance.